Dental cyst treatment
We treat dental cysts under a microscope
We perform tooth-saving operations
Painless, with local anesthesia or sedation
At Tetri’s Smile clinic, we treat cysts under a microscope without removing the tooth. We conduct precise diagnostics on a modern computer tomograph, and perform advanced tooth-saving operations. We have experience with treating cysts in the most complex clinical cases.
What is a tooth cyst?
A tooth cyst appears in the form of a round capsule (bag) with purulent contents. It forms in the bone tissue of the jaw in the background of an inflammatory-infectious process in the root canals. It is most often localized at the top of the root. Less commonly, it can be found on the side or in between roots.
At the initial stage, a small granuloma (3-5 mm) is formed. It gradually increases in size and fills with pus. It transforms into a cyst and continues to grow, leading to the atrophy of bone tissue. If located in the upper jaw, the infection can potentially spread into the maxillary sinuses. If located in the lower jaw, the infection can cause compression of the nerve, which can lead to serious consequences.
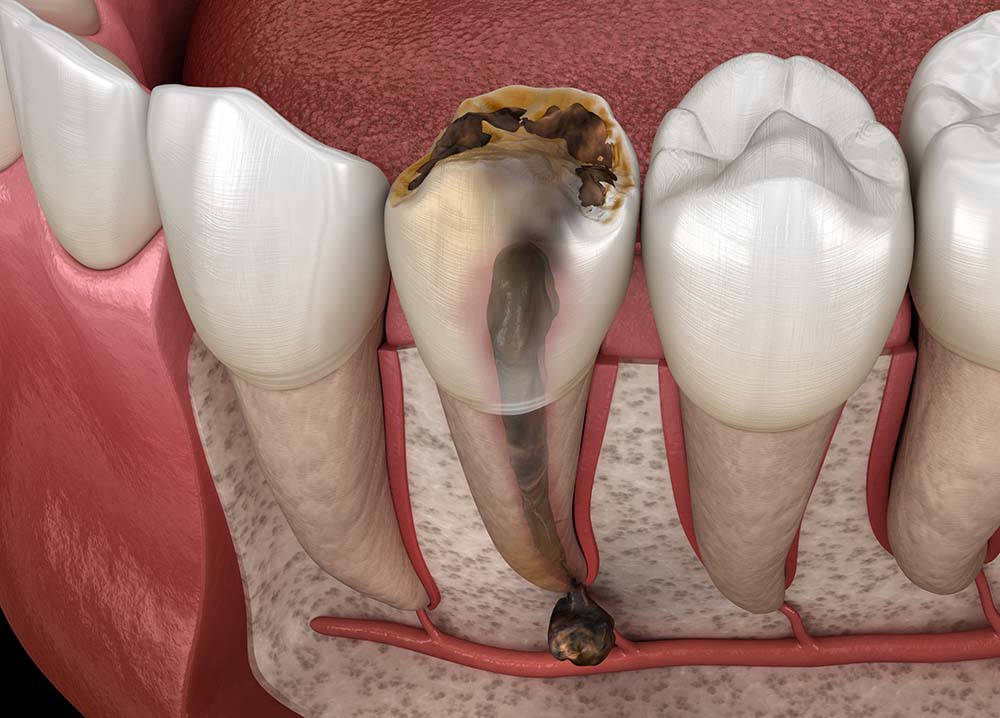
Dental cyst removal cost
Causes of tooth cyst formation
Pathogenic microorganisms in the affected carious tissues of the tooth penetrate deep inside, infecting the pulp. This leads to pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve).
If pulpitis is not treated, cariogenic bacteria settle in the root canals. They exit beyond the limits of the tooth through apical openings, leading to an infectious focus at the apex of the root. A granuloma is formed, which then transforms into a cyst.
After treating pulpitis / periodontitis, the dentist may not completely fill all of the root canals or their branches. Bacteria settle in the underfilled area, triggering an infectious process. When it exits beyond the root, it leads to the formation of a cyst.
Poor quality filling of branches / canaliculi becomes the cause of cyst formation on the lateral surface of the tooth root.
“When opening, passing and filling the canals of a tooth by an endodontist, precision is required. Without a dental microscope, it is impossible to exclude the risk that voids will remain, alongside a small piece of instrument that will remain in the canal.
In my practice of treating tooth cysts, I use a microscope, as well as many years of clinical experience in endodontics. As a lecturer and author of scientific papers, I am aware of the latest techniques. All this helps me achieve the best results in re-treating root canals.”
Symptoms of a tooth cyst
For a long time, a tooth cyst does not cause discomfort and remains in a “dormant” state. It practically doesn’t cause any sensations. However, the presence of a formation near the root can be suspected by the following symptoms:
Periodic discomfort or pain when biting on the affected tooth
Pain when pressing on the gum
Swelling of the gum in the projection of the root
An accurate diagnosis with determination of the localization and size of the formation is made after a computed tomography.
«Most patients do not experience any symptoms from a tooth cyst. This dangerous disease can go unnoticed for many months. More and more pus accumulates in the capsule, causing it to increase in size. Symptoms begin to appear, but some patients seek treatment too late and the tooth has to be removed.
There are also cases where I discover a cyst in a patient during a preventive examination or a CT scan before implantation. I recommend that everyone visit a dentist at least once a year for a preventive examination.»

Types of tooth cysts
Depending on the location, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
Radicular cysts can reach a large size – up to 3 cm. They are located at the apex of the root.
Periodontal cysts form on the side of the root in the gum tissue. Usually, they are small in size and can be successfully treated conservatively.
It forms when the integrity of the hard tissues at the bottom of the tooth cavity is violated. Often, the cause is a doctor’s mistake during the treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis, which resulted in perforation of the root canal.
A fistula filled with pus is formed. The patient may feel periodic tingling sensations.
Tooth cyst treatment
Depending on the clinical picture (cyst size, its location), the doctor decides on the choice of treatment method: conservative or surgical.
Conservative
With a small cyst (up to 7 mm), the following therapeutic treatment is carried out:
After anesthesia, the dentist opens the tooth, removes the nerve, and (if the roots have already been filled), removes the filling material. This opens access to the root canals.
The dentist fills the canals with a therapeutic paste. They check the quality of the filling with an X-ray, looking out for the presence of voids.
2-3 repeat visits may be required to replace the therapeutic paste until the cyst is completely eliminated.
When on one of the repeat X-rays, the volume of the cyst is close to zero, the dentist fills the root canals with gutta-percha and then restores the crown of the tooth.
Surgical
If the cyst is more than 8 mm in size, a surgical tooth-preserving operation is performed:
Under local anesthesia, the doctor forms access to the root canals.
Under a microscope, the new formation is opened. It is cleaned of pus and an antiseptic is applied. If necessary, the infected root tip is removed. In case of bone atrophy, osteoplastic material is applied. Stitches are applied.
A ceramic crown is placed, restoring the coronal part of the treated tooth
“The treatment of a tooth cyst primarily involves the work of an endodontist. If conservative therapy is not effective in saving the tooth, the assistance of a surgeon is required. However, the initial work of the endodontist can aid the surgeon in conducting a minimally invasive operation.
I collaborate with Dr. T. Gem Sayin, one of the best endodontists in Florida, working in my clinic. Together, we can help patients save their teeth even in severe cases.
Unfortunately, some patients seek dental assistance too late, and the cyst must be removed along with the tooth. In such cases, it is crucial to restore the lost bone volume to place an implant. I perform bone volume augmentation and then implantation.
No matter the clinical case, advanced cyst treatment can be done all under the roof of my clinic!”

Preventing Tooth Cyst Formation
This is an excellent way to prevent cavities, which are a common cause of cyst formation at the root tip.
It’s important to have a check-up to detect any cysts as early as possible, increasing the chances of removing them while saving the tooth.
If you have an infection in the root canal trust an endodontist who works with an operating microscope to perform the treatment.
FAQ
No, a cyst will not go away on its own. Simply taking antibiotics is not enough. Therapeutic or surgical treatment is necessary. The sooner you see a dentist, the higher the chances of saving the tooth from extraction.
As the cyst grows in size, it puts pressure on the bone tissue, leading to its atrophy. The tooth becomes loose and may eventually fall out.
The cyst may grow into the maxillary sinus or compress the inferior alveolar nerve, leading to dangerous consequences.
There is a high risk of the pus bursting out, causing blood infection and serious complications.
It is not recommended to place an implant in the socket of a recently extracted tooth with a cyst. There is a risk that it will not integrate properly. After removing the pus, it is better to wait for some time before undergoing tooth implantation.
Yes, but only in the case of a small cyst – up to 5 mm. The doctor will analyze the clinical picture and assess the likelihood of achieving a successful result with a course of antibiotic therapy.
More often than not, these formations are benign. However, there are rare cases of patients with malignant cysts. They are aggressive and rapidly increase in size, destroying bone tissue and displacing teeth. If a malignant cyst is suspected, the dentist will refer the patient for a consultation with an oncologist.

