Tooth pain after root canal treatment

After undergoing root canal treatment, discomfort may occur. You may wonder – Is this normal? Should I urgently see a dentist? How many days does the pain last after the procedure? When is it necessary to see the dentist again?
In this article, we will discuss the symptoms to pay attention to first, and what to do if the pain occurs some time after the treatment.
What should I expect after root canal treatment?
- Pain or sensitivity when biting or chewing. The dentist may prescribe pain medication during the recovery period.
- Sensitivity to cold or hot temperatures.
- Gum pain. The tissues may be irritated due to the dental procedures.
- Discomfort from a temporary filling. It may affect the bite. It will be replaced with a permanent filling in a few days.
Successful root canal treatment
Experiencing root canal tooth pain months or years after treatment?
Occurs when an infection sets in, causing inflammation at the root of the tooth. It may intensify or lead to other complications such as fever, swelling, sensitivity, or an abscess.
This symptom indicates tooth or restoration damage. It can be caused by a crack or fracture in the root, as well as damage to a filling or crown. It may be intermittent or persistent.
May arise following inflammation or improper nerve removal.
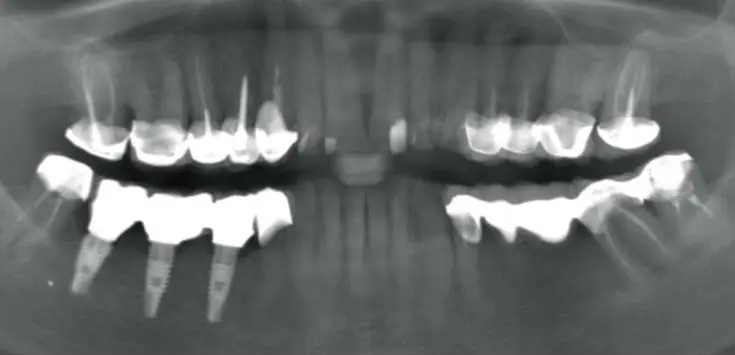
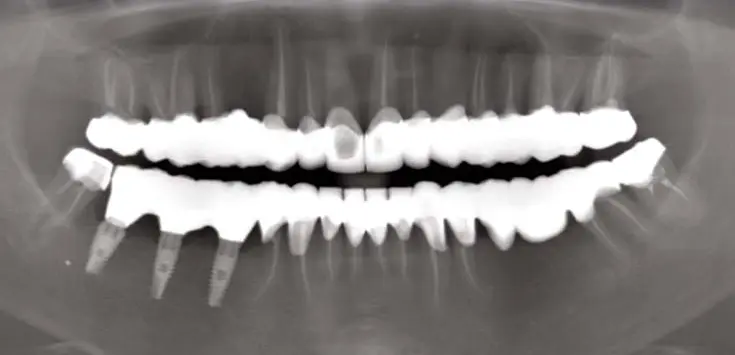
Example of a canal treatment
We received a patient who had already undergone root canal treatments for several teeth. However, the canal treatments were not done properly. Some of the dental canals were missed or not completely sealed.
Dr. Sain re-treated almost all of the canals – 20 in one day.
A year has passed, and the patient comes for preventive check-ups. Tooth pain no longer bothers her.
Experiencing tooth pain after root canal treatment? Here’s what to do
Have you noticed an increase in root canal pain or has it been bothering you for a long time? Make an appointment with a dentist immediately to avoid complications. Our endodontist will provide recommendations on how to reduce the pain and give you a plan of action before your visit to the clinic.
We often see patients from other clinics who are experiencing dull pain. We check for infections and any fragments from instruments. Sometimes the cause of the pain is deep-rooted and requires careful treatment.
During the treatment, we use a microscope to locate any branching or difficult areas in the canal. This helps us perform precise and painless treatment.
Tooth with root canal hurts with pressure or when biting
Treatment options for a tooth
If a filling was placed
If a crown was placed
Seek immediate retreatment at the clinic. The dentist will provide instructions to alleviate pain before the appointment:
- Advise on suitable pain medication.
- Prescribe antibiotics if signs of infection are present.
- Prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs in case of swelling.
Delaying the visit to the dentist will allow the infection in the root to progress, potentially leading to tooth fracture or gum inflammation. In severe cases, the dentist may recommend tooth extraction and implant placement. Therefore, do not postpone your dental appointment!

